🛑 Studies reveal that swallowing your partner’s semen… See more

1. Sperm Cells
-
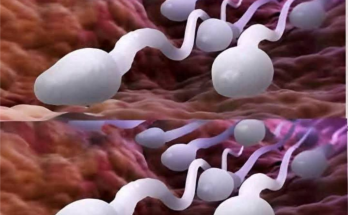
The most prominent feature in the image is the depiction of several sperm cells.
-
They have the classic shape:
-
Oval head: This contains the nucleus with tightly packed DNA, representing the father’s genetic contribution.
-
Midpiece (not clearly shown): In real sperm, this contains mitochondria for energy, powering the tail’s movement.
-
Tail (flagellum): Used for propulsion, enabling the sperm to swim through the female reproductive tract.
-
-
The image shows them swimming in the same direction, reflecting the biological journey toward the egg (ovum).

-
2. Background Tissue
-
The reddish-brown and pink background mimics the inner lining of the female reproductive tract.
-
The folds and textures suggest a soft, organic environment, likely either:
-
The cervical canal (initial entry point for sperm),
-
The uterus, or most likely,
-
The fallopian tube, where fertilization typically occurs.
-
-
3. Magnification and Artistic Touch
-
The image exaggerates the size and spacing to highlight the features of sperm cells, which in real life are microscopic.
-
Lighting and shading make the sperm appear three-dimensional, giving a semi-realistic yet digital feel.
-
The colors used are naturalistic enough to be educational but vibrant enough to engage a general audience.
Scientific Significance: The Journey of Fertilization
This image represents a critical phase in human reproduction: sperm migration and fertilization.
The Pathway of Sperm:
-
Ejaculation and Cervical Entry:
-
During ejaculation, millions of sperm are deposited in the vagina.
-
Only a few thousand survive the hostile acidic environment and pass through the cervix into the uterus.
-
-
Uterine Navigation:
-
Sperm are guided by chemical cues (chemotaxis) and uterine contractions toward the fallopian tubes.
-
-
Final Race in the Fallopian Tube:
-
Of the initial millions, only a few hundred reach the vicinity of the egg.
-
Only one sperm cell will ultimately fertilize the egg.
Fertilization:
-
When a sperm penetrates the egg’s outer membrane, it triggers a chemical reaction that prevents other sperm from entering.
-
The genetic material from the sperm merges with that of the egg, creating a zygote, the first stage of a new human life.
-
-
-